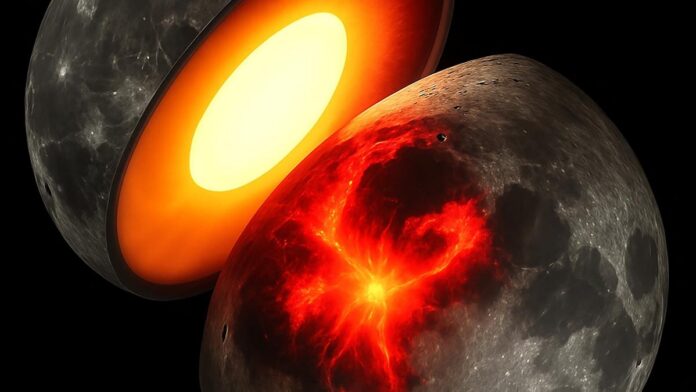
A concept by an undated artist shows the moon’s interior hot and volcanism around 2 to 3 billions years ago. It is believed that volcanic activity on Earth’s near side of the moon (the side facing Earth), helped create a landscape that is dominated by vast flat plains called mare. These are formed from molten rock which cooled and solidified. Photo Credit: NASA
NASA reveals hidden secrets of the Moon
Published:
A thorough examination of lunar gravity using the data obtained by two NASA robot spacecraft offers new clues as to why the two sides of moon – one always facing Earth and the opposite always facing away – look so different. The GRAIL mission of the U.S. Space Agency, or Gravity Recover and Interior Laboratory, has revealed that the deep interior of the moon is asymmetrical. This was caused by intense volcanism that occurred on its nearside millions of years ago, which helped shape the surface features.
The scientists discovered that the lunar nearside flexes a little more than the farside due to the gravitational pull of Earth. This is called tidal distortion. They said that this indicates differences between the two sides of lunar interior, specifically the geological layer known as the mantle. Ryan Park, supervisor of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory’s Solar System Dynamics Group and lead author of a study published in Nature on Wednesday, said
“Our study shows that the moon’s interior is not uniform: the side facing Earth – the nearside – is warmer and more geologically active deep down than the farside,” .
The nearside of the moon is covered with vast plains called mare. These were formed by molten rock which cooled and solidified millions of years ago. Its farside is more rugged, with fewer plains.
Some researchers have hypothesized intense volcanism on the nearside caused radioactive, heating-generating elements to collect on that side of mantle. This is what they believe is responsible for the surface differences observed. The new findings provide the strongest evidence to date in support of this hypothesis.
According to the researchers, the nearside mantle is on average 180-360 degrees Fahrenheit (100-220 degrees Celsius) warmer than the farside. The thermal difference may be caused by radioactive decay in the elements thorium or titanium on the nearside. Park said.
A moon with a diameter of 2,160 miles (3.475 km) is slightly larger than a quarter the size of Earth. The lunar mantle is a layer that lies beneath the crust, above the core and reaches a depth of about 22-870 mile (35-1400 km) below the surface. The mantle is about 80% of the mass and volume of the moon and is primarily composed of olivine and Pyroxene. This is similar to the Earth’s mantle.
“The fact that the detected asymmetry in the mantle matches the pattern of the surface geology – for instance, differences in the abundance of the approximately 3-4 billion-year-old mare basalts (volcanic rock) between the nearside and the farside – suggests that processes which drove ancient lunar volcanism are active today,” Caltech computational planetary scientists and study coauthor Alex Berne is affiliated with the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, working on the design gravity sensors for missions in the outer solar system.
Researchers spent years analyzing data collected by GRAIL’s Ebb and Flow satellite, which orbited around the moon between December 2011 and December 2012. Park said. Park added
“This enhanced gravity map is a critical foundation for developing lunar Positioning, Navigation and Timing (PNT) systems, which are essential for the success of future lunar exploration missions. By improving our understanding of the moon’s gravity field, it contributes to establishing a precise lunar reference frame and time system, enabling safer and more reliable navigation for spacecraft and surface operations,” . Researchers say that the same approach used here to assess the lunar interior using gravity data could be applied to other bodies within the solar system, such as Saturn’s Enceladus or Jupiter’s Ganymede. Both are worlds of interest to the search for possible life beyond Earth. The new findings will help us better understand Earth’s eternal partner. Park said. “Our knowledge of the moon has expanded through human and robotic missions that have revealed details about its surface and interior, yet many questions about its deep structure and history remain. As our closest neighbor, the moon continues to be an important focus of scientific discovery.”
Published on May 15, 2020




